ICH Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System

The stakes for quality management are high when it comes to the life science industry. As a result, pharmaceutical companies of all sizes need quality management systems built to address a slew of unique challenges and regulatory oversight. The key framework for creating a QMS that can handle the demands of the pharmaceutical industry is the International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Q10 model.
ICH Q10 was designed to model effective quality management for pharmaceutical and biotech companies, emphasizing innovation and continual improvement across the entire product lifecycle. ICH Q10 is not a binding regulation, but it can provide companies with a clear vision of what a robust pharmaceutical QMS should consist of.
Implementing a QMS that adheres to ICH Q10 pharmaceutical & biotech quality guidelines can help companies minimize the risk of suffering a devastating quality failure. In this post, we’ll detail the full scope and objectives of ICH Q10 and discuss how it comes into play at various stages in the product life cycle.
What is ICH Q10?
ICH Q10 is a framework developed by the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, an organization in which regulatory agencies and pharmaceutical companies work together to improve industry practices in the interest of public health.
ICH Q10 was shaped by regional Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations, guidelines from the International Standards Organization (ISO), and previous ICH guidelines. It is not designed to place additional requirements on top of existing regulations, but to better integrate the quality management process through the entire lifecycle of the product, from development to manufacturing. The goal of ICH Q10 is to encourage a paradigm shift away from separate GMP compliance processes at each step of the product lifecycle and toward a complete quality systems approach that spans the whole product lifecycle.
The ICH’s guidelines are applicable to companies that manufacture drugs, medicine, biotechnology, or any other pharmaceutical product. QMS solutions that utilize the ICH Q10 framework assist these companies in delivering safe products that consistently meet the highest expectations of quality and efficacy.
The Scope of ICH Q10 for Pharmaceutical Quality System
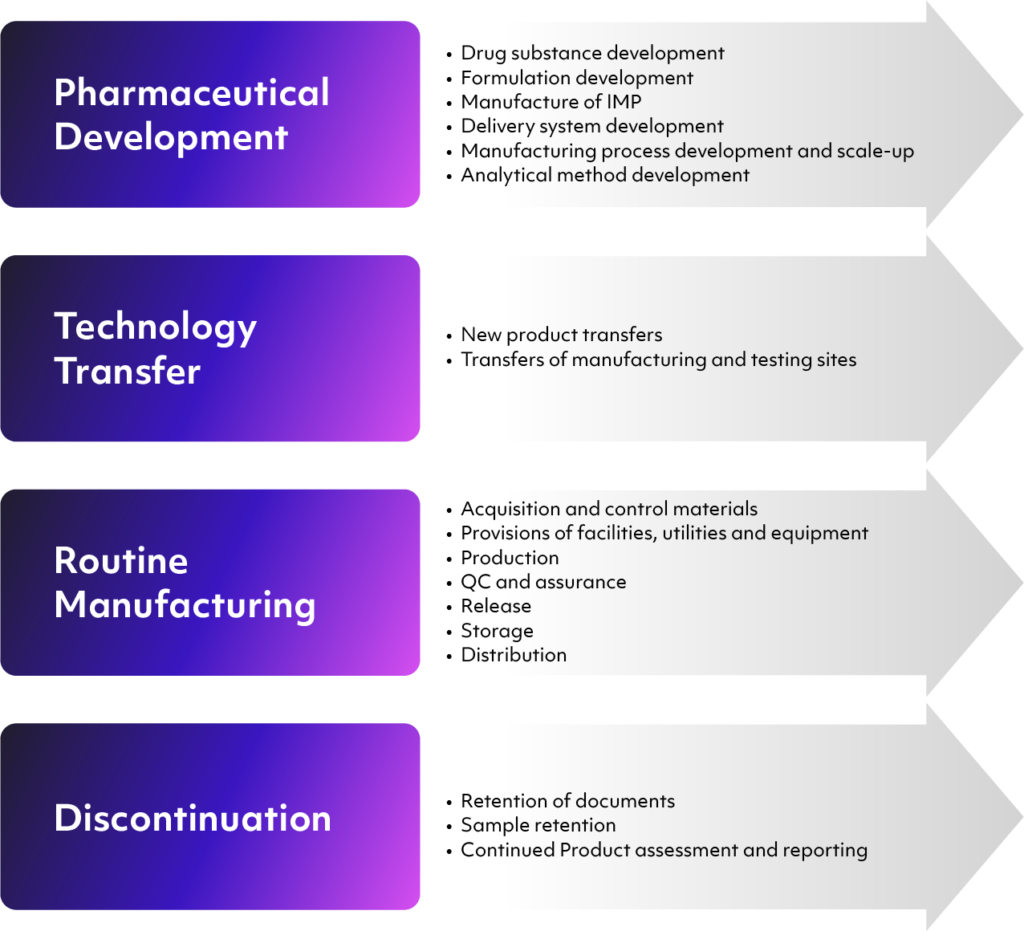
ICH Q10 is intended to incorporate, not exceed, regional manufacturing regulations. However, these regulations do not always cover every phase of the product’s lifecycle, such as its initial development. What ICH Q10 does is provide a framework for providing quality improvements based on solid scientific and risk-based concepts throughout the product’s entire lifecycle. Per the ICH, this includes the following stages:
- Pharmaceutical product development, including the initial development of the drug substance, investigational and analytical processes, the design of containers and delivery systems, and manufacturing processes
- Technology transfers at any point during the process — for instance, from development to manufacturing, or between manufacturing and offsite testing
- Commercial manufacturing processes, including materials acquisition, facilities and equipment, quality control and assurance, packaging, and distribution
- Product discontinuation in the event of a quality or safety issue, emphasizing document and sample retention and further monitoring
The Objectives of ICH Q10
With solid, GMP-based regional regulations assumed to be in place already, the objectives of ICH Q10 are focused on supporting the manufacturing process and creating opportunities to monitor and improve product quality.
There are the three primary objectives that should be met by implementing an ICH Q10 solution:
1. The Realization of the Product
The product is manufactured and delivered in a way that meets all applicable regulatory requirements. It meets the needs of the patients, medical workers, and other consumers who will be the product’s end users.
2. The Establishment and Maintenance of Control
Systems are put in place to monitor processes, assess product quality, and evaluate performance, thus demonstrating that manufacturing processes remain suitable and capable of meeting quality requirements.
3. Continual Product Improvements
Opportunities are identified and taken to innovate, improve processes and product quality, minimize variability, and enhance the QMS implementation. This maximizes your capability at any given time to deliver products of consistently high quality. Risk management methodologies are often employed to identify the areas with the highest need for improvement.
Product Lifecycle Phases Addressed by ICH Q10
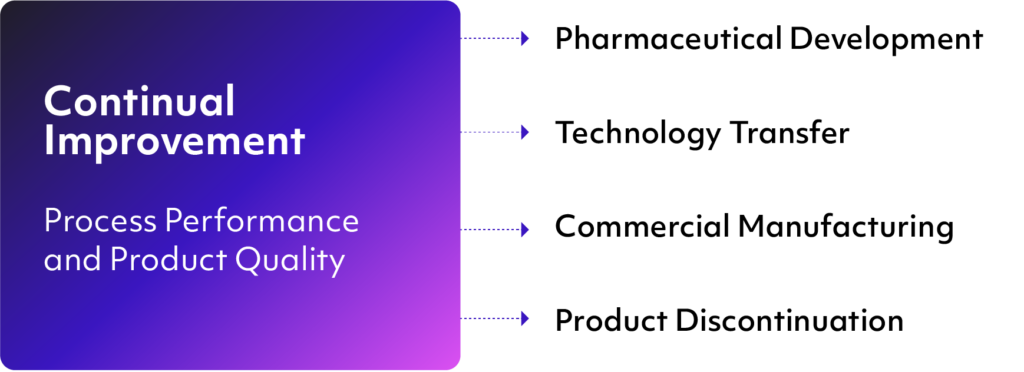
In addition to the above-listed objectives, ICH Q10 specifies four elements that are foundational to the guidance’s philosophy of facilitating continuous improvement throughout the entire product lifecycle.
In a QMS solution built around the ICH Q10 framework, the four elements are used to address various issues that might come up during product lifecycle phases outlined under the scope of the guidance. These are:
- Performance and Quality Monitoring can be applied at all phases to identify inefficiencies. The monitoring system should be on the lookout for product complaints (both internal and external) and should address commercial manufacturing issues by providing visibility into supplier performance and nonconformance events.
- Corrective Action and Preventive Action procedures should automatically take effect when issues are detected during manufacturing or after products have already been marked for recall. Following CAPA procedures are critical to identifying the true sources of quality issues, outlining the steps needed for correction, and documenting the process for future reference or compliance reasons.
- Change Management ensures that the steps needed to enact improvements are appropriately taken. The QMS can formalize and expedite the process of evaluating and approving changes.
- Managerial Review is needed to set priorities and approve changes at every phase. For management to make informed, timely decisions, it is essential to provide clear and comprehensive data. One crucial function of a QMS is to provide detailed, legible reporting on performance and quality data that can be used as a basis for sound decision-making.
ICH Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System
Product quality issues can always crop up where you aren’t expecting them. Still, even seemingly minor quality issues can be significant for smaller businesses in the pharmaceutical, biotech, and related life sciences industries. Building back your revenue, brand authority, and reputation can be costly and time-consuming.
This is why it’s so vital to have systems designed to eliminate errors, minimize risk, respond to feedback, and produce goods of the highest possible quality. ICH Q10 guidance buttresses this type of system with an emphasis on innovation, integration, and continual improvement, making it an essential part of successful pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturing processes (ICH Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality).
One of the most important tools for life sciences companies in this sector to have at their disposal is a robust QMS software solution designed to meet the needs of pharmaceutical and biotech manufacturing. Compatibility with the ICH Q10 model is one of the most reliable indicators that a QMS is right for pharmaceutical manufacturers and similar companies. It represents the above-and-beyond industry standard for companies who intend not just to meet the minimum regulatory mandates, but to provide top-quality products to their customers and engage in continual improvement to ensure that the level of quality never drops off.