
The life science sector is one of the country’s most lucrative industries. It’s currently worth $7.7 billion and is expected to attain a CAGR of 7.8% between 2021, and 2028.
But with huge rewards come huge risks, and the life science industries are abundant with them. From global volatility, intellectual property theft, to strict and evolving regulatory requirements, risks permeate nearly every facet of this sector, posing a constant threat to growth and success, and that’s why risk Assessment framework
Life science companies need to continuously implement and adjust their risk management and risk assessment protocols to survive. Companies must identify, assess, and manage these risks using industry standards and best practices and consider the unique circumstances that their product or service has for all stakeholders.
In this post, we will take a look at risk management for the life sciences industry, explore how to assess what risks need to be managed through employing a risk management framework, and the five necessary steps to building one that works for any organization.
Why Risk Management is Essential for Life Science Companies
For companies in the life sciences sector, risk refers to the probability of harm occurring and its potential severity. Common risk areas often include (but aren’t limited to):
- Cybersecurity
- Audit management
- Government pricing
- General data protection regulation
Risk management is the process of analyzing, evaluating, controlling, and monitoring risk through a systematic application of management policies, methods, and practices.
Effective risk management helps life sciences companies to accurately define when they will achieve their objectives, and appropriately respond to and plan for changing risk profiles.
A proactive risk management plan enables companies to stay compliant with the strict and elaborate market access regulatory requirements, allowing them to consistently gain approval for the commercialization of medical or pharmaceutical products and devices. It also allows them to address the increasing consumer demands for safer, risk-free medical breakthroughs.
Key Risk Management Regulations
There are many risk management regulations and compliance standards in the life sciences industry that must be followed to successfully maintain business operations and ensure the safety of staff and product users.
Key risk management regulations for Life Sciences companies include:
ISO 12485:2016
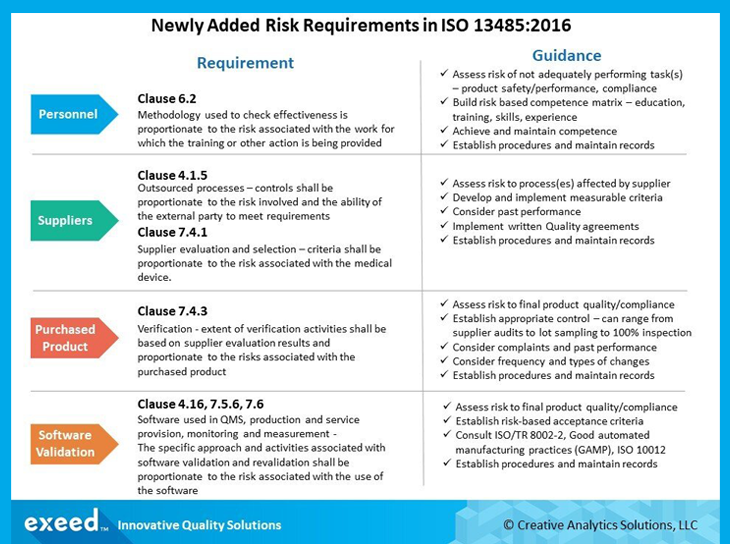
This internationally recognized standard was revised and published in 2016. ISO 13485:2016 applies to manufacturing medical devices and also all associated services offered by the manufacturing organization.
It specifies quality management standards for organizations that design, produce, install and service medical devices. It mainly focuses on risk-based decision-making, and the changes brought about by dynamic regulatory requirements for Life Science companies in the supply chain.
ISO 14971:2019
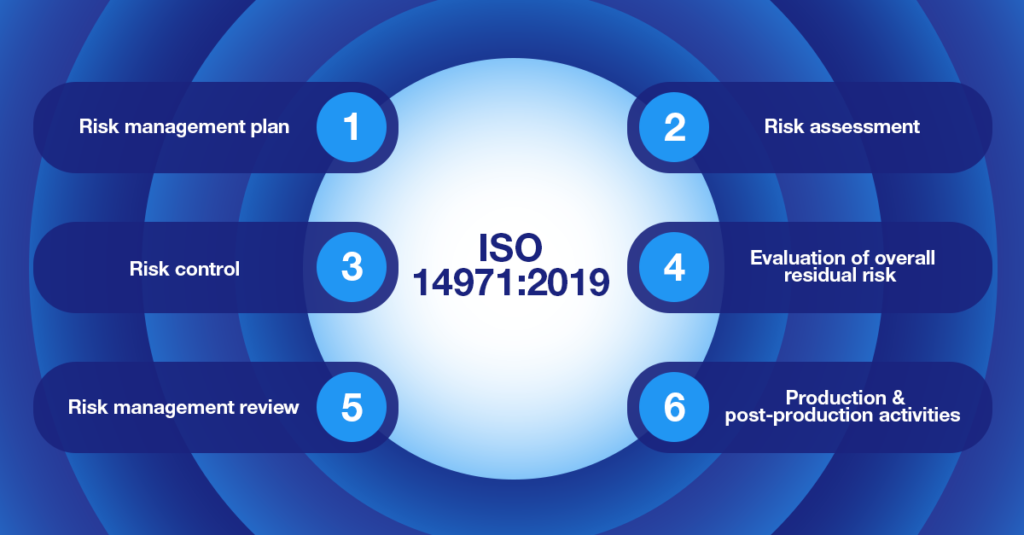
The ISO 14971:2019 regulatory standard covers the principles and processes that medical device manufacturers should use to perform risk management on their products.
This standard aims at helping manufacturers evaluate the risk associated with their devices, how to control it, and how to monitor the efficiency of applied solutions. ISO 14971 applies to all phases in the life cycle of a medical device but does not require manufacturers to have a quality management system in place.
EU MDR 2017/745
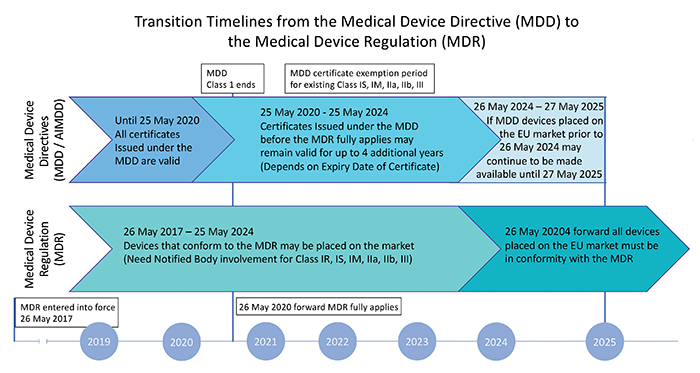
The European Union Medical Device Regulation (Regulation (EU) 2017/745, MDR) establishes the restrictions and requirements on the manufacturing and design of medical devices. It ensures any medical device available for sale in the EU market is safe and can function as intended.
The standard was updated in 2017 to replace Directive 93/42/EEC and Directive 90/385/EEC and covers all medical devices, parts of, or materials used in these devices that might be invasive, or are used to administer medicine, transport, or store bodily fluids, and other similar substances.
FDA’s Safer Technologies Program (SteP) for Medical Devices
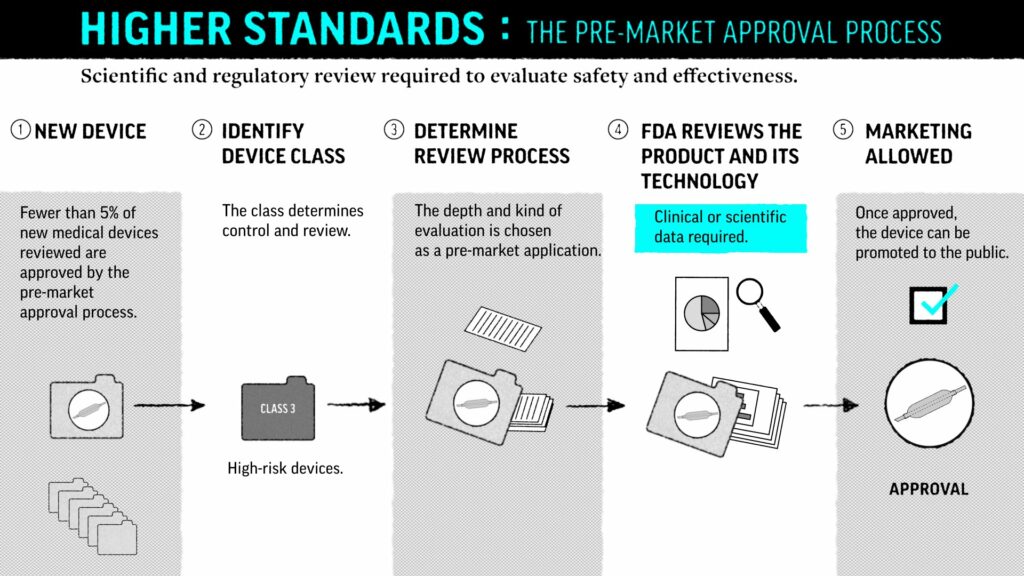
The Safer Technologies Program (SteP) is a new, voluntary FDA program for medical devices and device-led combination products that enhance the safety of treatments for non-threatening conditions. The program is modeled after the FDA’s Breakthrough Device Programs (BDP) and helps reduce the time to develop and gain market approval for such devices.
While these regulations go a long way in improving compliance and manufacturing of quality medical devices, risk management is only effective if the risks that need managing are known. Here’s where risk assessment comes into the picture.
What is risk assessment?
Risk assessment is the process of identifying probable hazards, the likelihood of occurrence, the impact, and how well a life sciences company can respond. Risk assessment includes an analysis and evaluation process during which available data is used to identify potential risks and analyze overall risk acceptability based on defined criteria.
Assessment is the first step in risk management and essential to the process because it helps organizations:
- Create awareness about a hazard, and identify who’s at risk
- Determine whether control measures are necessary
- Identify whether existing measures are sufficient
- Establish control measures
- Skip the costs of unnecessary risk management
- Meet and reduce legal liabilities where applicable
The question for an organization becomes, how do we consistently assess risks? The answer is to establish a risk assessment framework.
5 Necessary Steps for Building a Risk Assessment Framework
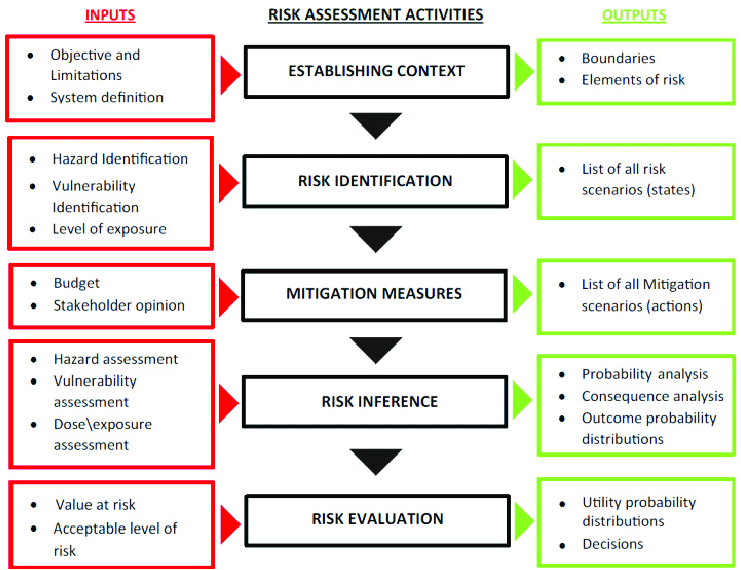
A risk assessment framework is a system to help understand and evaluate organizational risks and efficiently share information about these risks with other members. Here are the five necessary steps to creating an efficient one that will be a good fit for any organization’s unique needs:
1. Risk Identification
The first step in building a risk assessment framework is to determine potential hazards and risks. When it comes to recognizing these dangers, having relevant, appropriate, and up-to-date information is critical.
Professionals are advised to evaluate factors such as threats and opportunities, knowledge limitations, vulnerabilities, tangible and intangible risk sources, and even biases or assumptions of involved parties.
2. Risk Analysis
Once the potential risks are identified, the next step is to conduct a risk analysis to prioritize the right course of action based on existing measures or to determine the likelihood of occurrence, its impact, possible controls, and their efficiency. An analysis is critical because some risks have multiple causes, and cannot be alleviated unless all culprits are addressed.
Review work routines and processes for each hazard identified to determine who inside and outside the organization might be harmed and how. Remember to assess how these potential risks may affect visitors, clients, and members of the public.
3. Risk Evaluation
The next step is to evaluate any risks that have been identified and analyzed. If a hazardous situation is identified, an evaluation must occur to determine its probability and potential severity.
Use of a risk matrix can help organizations prioritize which risks are most substantial, and therefore require immediate action or further allocation of resources. Evaluating and prioritizing risks in this way helps organizations determine risk acceptability and the level of reduction strategies to implement.
4. Risk Communication
Life sciences companies are required by law to record findings in situations where five or more staff members participated in risk evaluation. The findings should offer more hazard details while highlighting those at risk and any reduction strategies implemented.
Risk evaluation documentation, including possible precautions and solutions, is a crucial part of a successful framework. The easiest way to document and keep track of these risks is by using a robust quality management system (QMS). Risk management, compliance, and safety are increased throughout an organization when there is a central hub for all risk assessment findings.
5. Review and Adjust
Just like any organization, risks are always changing. It’s prudent to review the organizational risk assessment framework regularly to ensure proper management and compliance measures are still being applied, and adjust as needed to cover new policies, work practices, and regulations.
Risk Assessment, Management, and QMS
By employing a consistent risk assessment framework, life science organizations have a way to identify, analyze, evaluate, and document risks that might interfere with product compliance or safety. Using the five steps listed above will help an organization develop a framework that fits their unique needs. In an industry full of uncertainty, successful risk assessment ensures better outcomes for risk management strategies that alleviate the probability of mishaps occurring and improve the organization’s bottom line.
Using QMS automates the risk management process, easing compliance issues by organizing and simplifying the documentation process. It also facilitates evidence-based decision-making, allowing a life sciences organization to continuously improve existing risk management measures and reduce the likelihood of recurring issues in the future.

